With AMD finally announcing the RX 6000 series graphics cards, featuring their new RDNA2 architecture, they have managed to close the gap between themselves and Nvidia, the top video card manufacturer in the market. Although Nvidia released their RTX 3000 series GPUs based on the Ampere architecture a while ago, the lack of supply has prevented them from being able to ship cards to customers. So this holiday season, the question arises among many PC building enthusiasts: AMD RX 6000 vs. Nvidia RTX 3000 Series GPUs.
With several options available, it can get quite confusing to find the best card for your system. In this comprehensive guide, we will try our best to provide a detailed comparison between the two series of cards, going through a case-by-case basis over every specification and help you decide which one you should buy?
Specifications
| Stream Processors | Base/Boost Clock | Memory | Memory Clock | Power Connectors | Outputs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RX 6800 | 3840 | 1372/2105 MHz | 16 GB | 16 Gbps | 2x PCIe 8- pin | 1x HDMI 2.1, 2x DisplayPort 1.4a 1x USB Type-C |
| RTX 3070 | 5888 | 1500/1725 MHz | 8 GB | 14 Gbps | 2x PCIe 8- pin | 1x HDMI 2.1, 3x DisplayPort 1.4a |
| RX 6800XT | 4608 | 1487/2250 MHz | 16 GB | 16 Gbps | 2x PCIe 8- pin | 1x HDMI 2.1, 2x DisplayPort 1.4a 1x USB Type-C |
| RTX 3080 | 8704 | 1440/1710 MHz | 10 GB | 19 Gbps | 2x PCIe 8- pin | 1x HDMI 2.1, 3x DisplayPort 1.4a |
| RX 6900XT | 5120 | 1429/2250 MHz | 16 GB | 16 Gbps | 2x PCIe 8- pin | 1x HDMI 2.1, 2x DisplayPort 1.4a 1x USB Type-C |
| RTX 3090 | 10496 | 1890 MHz/2437 MHz | 24 GB | 19.5Gbps | 3x PCIe 8-pin | 2x HDMI 2.1, 3x DisplayPort 1.4a |
Performance differences between the RX 6000 and RTX 3000 Series Processors
Before we dive into the benchmarks comparing the performance between the two series of graphic cards, it is essential to note that the test bench used for the AMD cards used a Ryzen 9 5900X, which features AMD’s Smart Access Memory technology allowing the CPU to access the VRAM of the AMD GPU for a maximum performance increase of up to 11%. This feature does not support Nvidia cards.
In 4K gaming, over an average of 10 games, the Radeon RX 6900XT manages to beat the GeForce RTX 3090, while the RX 6800XT beats the RTX 3080. The RX 6800 manages to surpass last year’s RTX 2080Ti by a respectable margin.
4K gaming is pretty VRAM intensive, so games like Wolfenstein Youngblood and The Division 2, which can make use of the faster GDDR6x VRAM present in Nvidia cards, show significant performance improvements over AMD. The remaining games at 4K are not that VRAM-intensive, so the Nvidia cards lose their advantage, and the AMD cards offer a considerable performance gain in most titles, especially with the RX 6800XT beating the RTX 3090.
In WQHD gaming, the RX 6900XT and RX 6800XT beat the Nvidia cards in the ten games average performance, while the RX 6800 comes close to the RTX 3080.
In WQHD gaming, the faster VRAM of the Nvidia cards does not give them the advantage to beat the AMD cards since gaming in WQHD is not VRAM-intensive, thereby allowing the top two AMD cards to be equal to or better than the RTX 3090.
The performance results of these cards are not yet final since the comparison of these benchmarks on an Intel platform should help increase Nvidia cards’ performance. These results still show that the RX 6000 series are the clear winners when it comes to performance per dollar since the $679 RX 6800XT beats the $1499 RTX 3090, especially in WQHD gameplay. By using the already powerful Ryzen 5000 series chipset with a 500 series motherboard, you should be able to get a robust setup that gives you the best value for your money.
Memory configurations between the RX 6000 and RTX 3000 Series Processors
| Memory Configuration | RX 6000 series | RTX 3000 series |
|---|---|---|
| Type | GDDR6 | GDDR6x |
| Bandwidth | 512.0 GB/s | 448.0 GB/s, 760.3 GB/s, 936.2 GB/s |
| Bus | 256 bit | 256 bit, 320 bit, 384 bit |
| Size | 16 GB | 8 GB, 10GB, 24GB |
Pricing differences between the RX 6000 and RTX 3000 Series Processors
| AMD | Price | Nvidia | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| RX 6800 | $580 | RTX 3070 | $500 |
| RX 6800XT | $650 | RTX 3080 | $700 |
| RX 6900XT | $1000 | RTX 3090 | $1500 |
Power and efficiency differences between the RX 6000 and RTX 3000 Series Processors
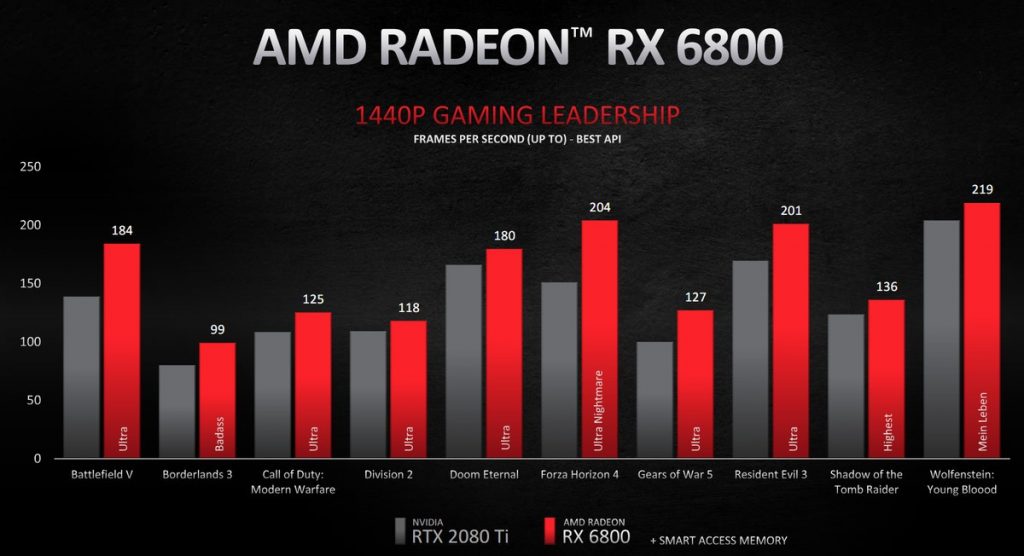
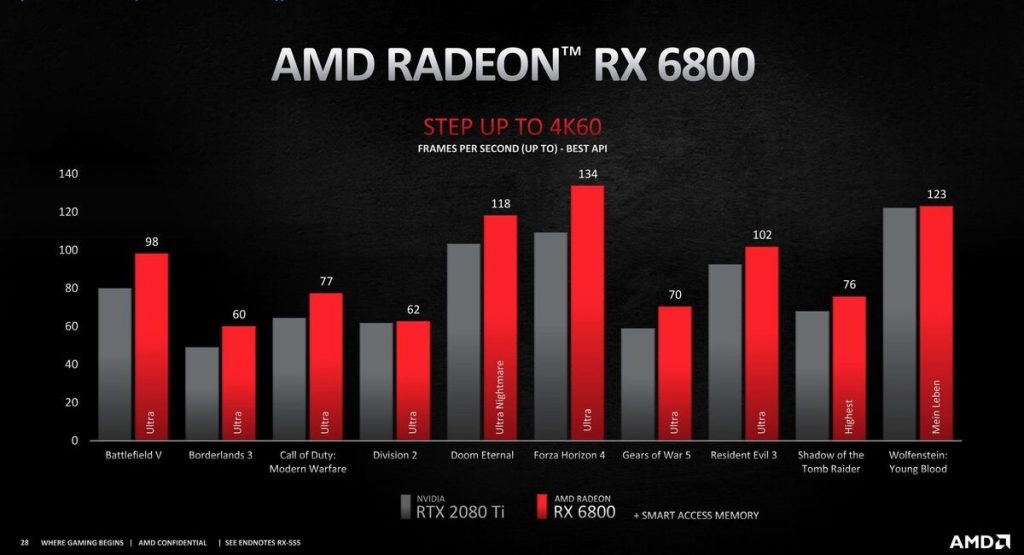
The 6800 with a power draw of 250W manages to consistently beat the RTX 2080Ti flagship GPU from last year in most 1440p titles. As for 4k gaming, it does keep the lead in most titles. The RTX 3070, on the other hand, with a total power consumption of 220W, comes close to the RTX 2080Ti in 1440p games and pulls ahead in several 4k titles. However, the 2080Ti is still the superior GPU between the two.
The 3070 offers performance in league with the 6800, but some testing is still required to determine the more efficient card, especially in 4k gaming. However, the 6800’s excellent performance in 1440p gaming, where it beats even the RTX 3090 in titles like Forza Horizon 4, makes it pretty efficient for gaming at such settings.
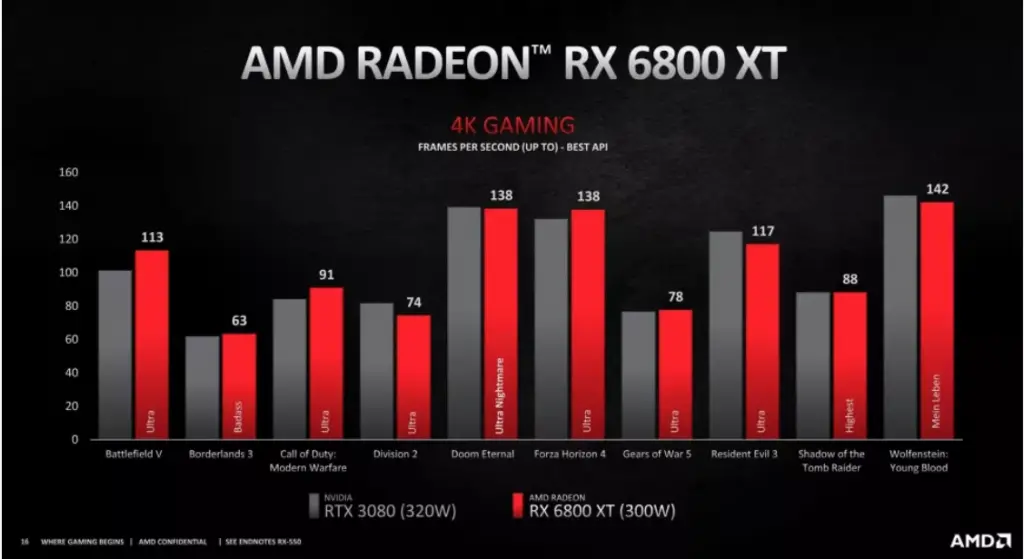
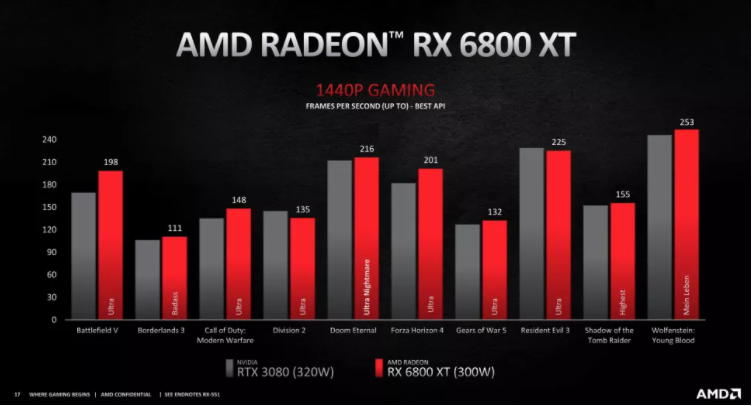
The RX 6800 XT with a 300W TDP manages to keep up with the RTX 3080 with a 320W TDP in 4K gaming and has a substantial lead over it in 1440p gaming, gaining a slight efficiency advantage over the RTX 3080.
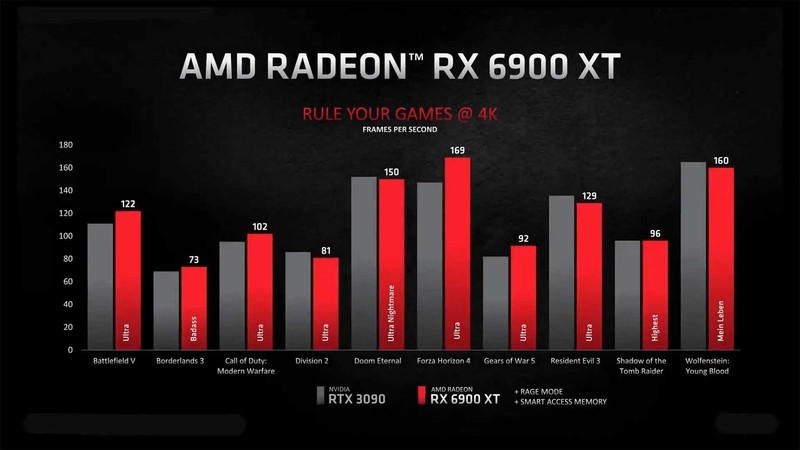
The same can be said for the RX 6900XT with a 300W that again manages to beat the 350W RTX 3090 in several 4K titles, and all of the WQHD ones. The efficiency gain over here is quits significant considering it performs better while using 50W lesser than the RTX 3090.
Additional technology differences between the RX 6000 and RTX 3000 Series Processors
| RX 6000 series | RTX 3000 series |
|---|---|
| Infinity Fabric: On chip cache similar to the L3 cache on a CPU, that reduces the dependence on VRAM, greatly increasing bandwidth and improving efficiency. | GDDR6x memory: Improved signal transmission design that doubles the data rate per clock, increasing efficiency and performance by increasing data per clock. |
| Ray Accelerator: A high performance, fixed-function engine that enables RDNA2 to support DX Ray Tracing. | 2nd Generation Ray Tracing Cores & 3rd Generation Tensor Cores: Dedicated processing cores on the GPU specifically designed to tackle performance-intensive ray tracing workloads. Tensor cores help power Nvidia DLSS for accelerated gaming performance. |
| AMD Smart Access Memory: Allows Ryzen 5000 series processors to directly access GDDR6 memory, improving gaming performance by up to 13% | RTX I/O: The Nvidia GPU directly offloads data from the SSD preventing the CPU from bottlenecking decompression and other processes improving loading speeds. |
| DirectX® 12 Ultimate: Support for hardware accelerated ray-tracing and VRS which is the prioritization of rendering based on optimizations to improve performance. | NVIDIA Reflex: A suite of GPU, G-SYNC display, and software technologies that allow for optimization of system latency. |
Final Thoughts
With AMD GPUs now supporting DirectX Ray Tracing, it has finally become a viable option to buy an AMD GPU over Nvidia’s options. Based on the results provided by AMD, the Radeon GPUs’ gains in performance and efficiency over Nvidia make them the go-to choice for most gamers, especially the RX 6800XT, if you’re looking to get a high framerate on a 1440p resolution. If you’re looking towards 4K gaming, then the RX 6900XT is the right choice, both for its price and efficiency.
As of right now, the Nvidia cards are still pretty scarce, and if AMD manages to have an adequate supply of GPUs, Nvidia will surely see a massive chunk of the market taken away from them. We would still recommend waiting for the comparisons on an Intel platform for both GPUs before making a decision, so it’s best to wait till you have all the options in front of you.



