When purchasing a CPU, the socket is a major factor to consider. Both Intel and AMD have different types of surface mount technologies (SMT) that define how their processors connect to the socket on motherboards. The two most popular CPU sockets on the market today are the LGA and PGA.
Therefore, If you’re thinking about upgrading or buying your first processor and haven’t yet decided if LGA or PGA is right for your computer, then you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll be examining the differences between the LGA and PGA CPU sockets to find out which is better for you.
What Is A CPU Socket?
A CPU Socket is a physical interface between a central processing unit (CPU) and accompanying integrated circuits, memory, and other components. This socket provides electrical and mechanical connections between the CPU and the computer motherboard, allowing for the insertion and removal of CPUs.
The term “Socket” is also used to refer to the socket on the motherboard that the CPU plugs into. There are different types of CPU sockets, with the most common being the LGA (land grid array) and PGA (pin grid array) sockets. CPUs come in different sizes and shapes, so the socket must be compatible with the CPU.
LGA (Land Grid Array)
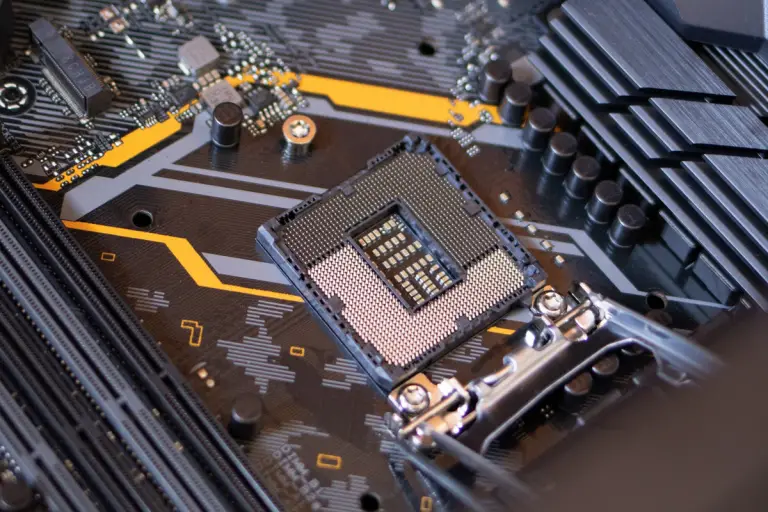
An LGA socket is used to connect a CPU to a particular type of motherboard. It is an IC (Integrated Circuit) surface mount technology used primarily by intel. The LGA socket pins are located on the motherboard and arranged in a grid-like pattern hence the name Land Grid Array. This can be seen in the image of an LGA socket provided below. The pin arrangement in this socket means that it can be reused over time with other compatible CPUs as well.
Moreover, from the image of an LGA CPU below, you can see that the CPU itself has no pins. Instead, it has metal pads that contact the pins of the LGA socket on the motherboard. In short, LGA motherboard sockets have pins while LGA CPUs have pads that contact the corresponding pins of the socket when installed properly.
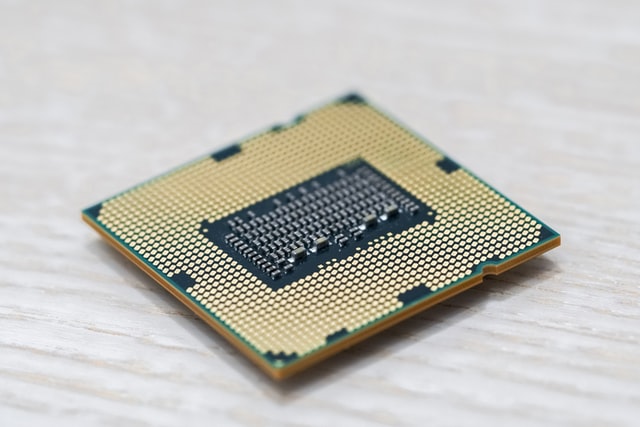

Pros of LGA Socket
Reliable Connection: The major advantage of an LGA socket is that it provides more reliable contact between the CPU and the motherboard due to its more dense pin arrangement.
Space Efficiency: LGA pins are significantly thinner than PGA pins allowing for more space efficiency.
Cons of LGA Socket
Bending/breaking a pin: Incorrectly installing an LGA socket may lead to a bent or even worst a broken pin on the motherboard socket meaning you would have to possibly replace the whole motherboard.
Harder to repair: It is harder to repair LGA socket pins on a motherboard than it is to repair the thicker more durable PGA CPU pins.
Intel LGA sockets and CPU Compatibility
Most LGA sockets are designed to be compatible with an array of different processors and work with multiple generations of processors. Therefore, it’s important when buying a new motherboard for your computer (or for use in building one) to make sure it has the proper compatibility with the CPU you plan to pair it with:
- LGA 1151 for 7th, 8th, and 9th Gen Core, Pentium, and Celeron CPUs
- LGA 1200 for 10th and 11th Gen Core, Pentium, and Celeron CPUs
- LGA 1700 for 12th Gen Core, Pentium, and Celeron CPUs
PGA (Pin Grid Array)
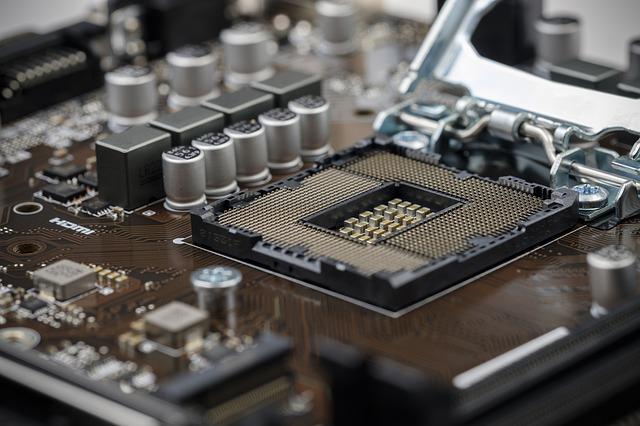
A PGA socket is a type of surface mount technology used to connect a CPU to a particular type of motherboard. PGA sockets are primarily used by AMD though their HEDT platform uses LGA sockets. Unlike LGA, PGA sockets on the motherboard do not have pins, but instead, have tiny holes that correspond to each of the pins located on the PGA compatible CPU. Therefore, you can think of a PGA socket as the opposite of an LGA socket in which the pins are on the processor chip rather than the motherboard socket as you can see from the image provided below.

PGA sockets are typically made from an electrically conductive material, such as brass or copper. They are also usually plated with a material that is resistant to corrosion, such as gold or nickel. The pins on the PGA CPU seen in the image provided below are inserted into the corresponding socket holes on the motherboard. This type of connection is very reliable and ensures that the CPU is properly seated in the socket.
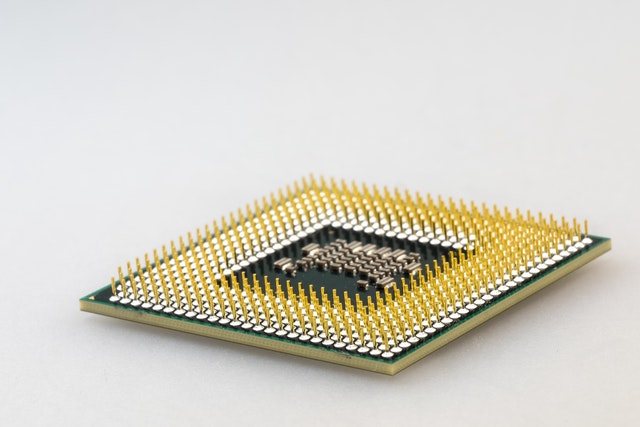
Pros of PGA Socket
Easy to install: PGA sockets are easy to install and use, even for those who are not tech-savvy. This makes them ideal for anyone who wants to upgrade their CPU without having to go through a complicated installation process.
Greater Mechanical Stability: PGA sockets have a more robust design than other types of IC sockets. This makes them less likely to break or become loose over time.
Cons of PGA Socket
Damaging a pin: One damaged pin can render the entire CPU useless. This could cost you more when using PGA sockets because CPUs are generally more expensive than motherboards. Therefore, having to replace a damaged PGA CPU with broken pins rather than a damaged LGA motherboard socket with broken pins could be more expensive.
LGA vs PGA comparison table
We’ve included this comparison table so you can understand the differences between LGA and PGA more easily.
| Criteria | LGA Socket | PGA Socket |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Intel processors | AMD processors |
| Build Quality | Good | Better (thicker less dense pins) |
| Space Efficiency | More | Less |
| Durability | Fairly durable | Slightly more durable |
| Installation | Fairly easy | Easier |
Differences between LGA vs PGA sockets
LGA and PGA sockets are two different types of sockets used for connecting processors to motherboards. Here are the main differences between the two:
- LGA is common on Intel while PGA is common on AMD
- LGA has pins on the motherboard while PGA has the pins on the CPU
- PGA is easier to install, as the pins tend to be thicker (more durable)
- PGA pins are more durable and therefore easier to fix than LGA motherboard socket pins
Compatibility
Although PGA and LGA sockets are both used for processors, they are not interchangeable. This is because the two types of processors use different pin layouts. LGA sockets are typically found on Intel CPUs, while PGA sockets are typically found on AMD CPUs.
Build Quality
LGA sockets have pins on the motherboard’s socket while the CPU has contact pads without pins. LGA sockets have a couple of advantages over PGA sockets. First, they typically have more pins than PGA, which provides a more reliable connection.
While PGA sockets, on the other hand, have pins protruding from the CPU that correspond to each whole on the socket of the motherboard. PGA has thicker pins making the CPU easier to install into the motherboard, which can be helpful for novice users. Those thicker and less dense pins also make it easier to repair than compared to LGA. In terms of build quality, then, PGA sockets are generally slightly superior to LGA sockets.
Space Efficiency
LGA pins are significantly thinner and denser than PGA pins, which offers several advantages in terms of space efficiency. In particular, LGA pins allow for more space efficiency, which is always desirable in terms of space utilization. In addition, the denser-packed LGA pins also offer better electrical connectivity.
Durability
While both LGA and PGA sockets are designed for durability and longevity, some key differences between the two may impact their overall lifespan.
LGA sockets have a higher pin density than PGA sockets, which means that they are more likely to experience pin damage and wear over time. While PGA CPUs, on the other hand, have thicker less dense pins making them less likely to experience pin damage. In general, both LGA and PGA sockets are quite durable and should last for many years with proper care.
Installation
LGA and PGA sockets are two common types of sockets used in computer processors. While they both have their advantages, they can also pose some difficulties during the installation.
LGA (land grid array) sockets are densely designed with the pins being on the motherboard socket with the processor sitting on top of them. This can make it difficult to align the processor correctly during installation. PGA (pin grid array) sockets are easier to install due to the thicker less dense processor pins. This makes it easier to install the PGA processor, but it can also be more difficult to remove or replace it.
LGA vs PGA: Which is the best choice for you?
LGA (Land Grid Array) and PGA (Pin Grid Array) are two common types of CPU sockets. They are both used to connect a CPU to a motherboard, but they differ in a few key ways.
The main difference between LGA and PGA is the way that the CPU is connected to the socket. LGA motherboard sockets have pins that connect to corresponding contact pads on the CPU. While PGA motherboards have holes in the socket that connect to the corresponding CPU’s pins when inserted.
So, which type of socket is best? LGA or PGA? The answer is both LGA and PGA are good CPU socket options as you can’t really good wrong with each. They each have their benefits and drawbacks. But you shouldn’t choose a CPU and motherboard based on just its socket. You should choose them based on the performance you desire, the budget you have to acquire, and the availability of those components. This could lead you to an LGA (Intel) or PGA (Generally AMD) system based on your computational needs.
LGA and PGA FAQs
What are LGA and PGA on a motherboard?
LGA and PGA are two types of sockets used on motherboards. LGA stands for land grid array, and PGA stands for pin grid array. Both types of sockets are used to connect the CPU to the motherboard. LGA Motherboard sockets have pins while the CPUs have contact points without pins. And vice versa, PGA Motherboard sockets have holes (no pins) while the CPUs have pins that correspond to those holes.
Which one is better, PGA or LGA?
Ultimately, the best socket for you will depend on your budget and your needs. If you’re looking for a high-performance CPU, then an LGA socket is the way to go. But if you’re on a tight budget, then a PGA socket may be a better option.
Does Intel use LGA or PGA?
There is no easy answer to this question, as Intel has used both LGA and PGA sockets for its processors over the years. However, it seems that the majority of Intel processors these days use the LGA socket. This is the type of socket that is typically used for desktop processors, so it makes sense that Intel would continue to use this socket for its newer processors.
Does AMD use LGA or PGA?
There is some confusion about whether AMD uses LGA or PGA, but the answer is both. AMD uses both LGA and PGA sockets, depending on the specific processor model. For example, some of the newer Ryzen processors use an LGA socket, while older models use a PGA socket. So, it depends on the processor model in question. In general, though, AMD does use both LGA and PGA sockets.